NFC Business Cards
With DigiPromoting, you can turn your digital business card into a Near-Field Communication [NFC] device in seconds, all you need is an NFC tag. The Tag is then embedded into a stylish devise of your choice for ease of use.
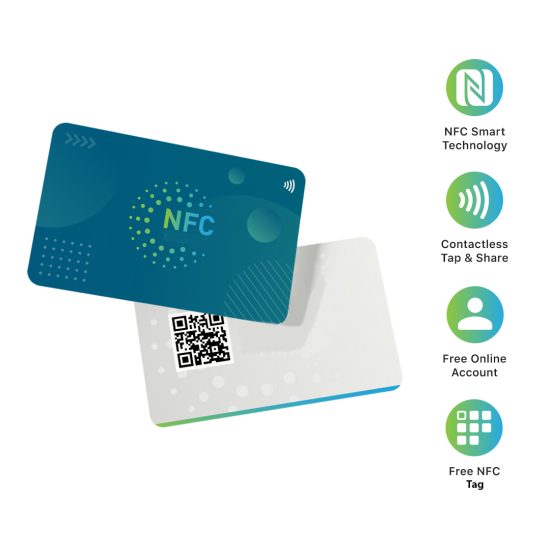

What is an NFC business card?
NFC tags come in several forms, like stickers, pop sockets, keychains, and physical cards. They contain tiny microchips, and when tapped to another smartphone, the information paired with your tag (like the link to your business card) automatically appears.
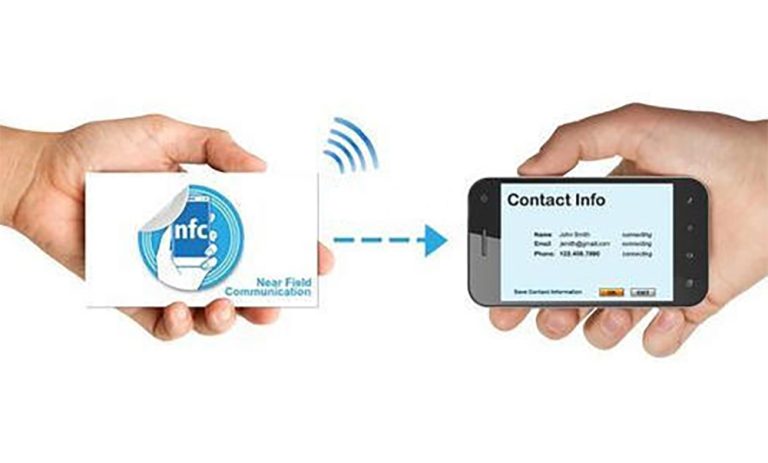
Near-field communication (NFC) business cards enable you to share your contact information with a single tap. NFC business cards have two components: a digital business card and an NFC tag.
What Are NFC Tags? A Guide
The popularity of smart devices has skyrocketed in recent years. And the more powerful smart devices become, the more we can use them to interact with our environment. A seamless user experience for connected living needs efficient solutions to transmit data and trigger events — near-field communication (NFC) is one of the elements that enables devices to connect with each other to exchange data.
What Are NFC Tags?
Near-field communication technology allows two devices to communicate wirelessly. The technology can be embedded in a small tag to facilitate data transfer between nearby mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and other electronics. NFC tags are often compared to RFID, but the two are different.
What is RIFD?
The RIFD technology (radio-frequency identification) is the predecessor of NFC. RFID tags are most commonly known from anti-theft systems attached to the more expensive products in stores. RIFD has been successfully used to track inventory in a variety of sectors and industries, e.g., manufacturing, healthcare, automotive, or apparel — wherever there’s a need to track items.
What is NFC?
NFC is part RFID (radio-frequency identification) and part Bluetooth. Unlike RFID, NFC tags work in close proximity, giving users more precision. NFC also doesn’t require manual device discovery and synchronization as Bluetooth Low Energy does. The biggest difference between RFID and NFC is the communication method.
RFID tags have only a one-way communication method, meaning an RFID-enabled item sends a signal to an RFID reader.
NFC devices have a one- and two-way communication capability, which gives the NFC technology an upper hand in use cases where transactions are dependent on data from two devices (e.g., card payments). Mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, Android Pay, and other contactless payment solutions are all powered by the NFC technology.
So in essence, RFID tags are great for inventory tracking and NFC tags work well for enhanced communication.
How Do NFC Tags Work?
NFC tags work like any other RFID tag to communicate over radio waves. Two devices — the NFC tag and the NFC reader exchange information in NFC data exchange format.
An NFC tag sends radio waves to activate the antenna in a receiving device. The recipient validates the information to complete information exchange.
The technology works over a very short distance — approximately 4 inches. NFC tags work without a battery and draw power from another device, e.g., a smartphone.
An NFC reader connects to only one NFC tag at a time, minimizing accidental transactions. During NFC payments, encrypted data exchange happens between NFC chips. Card details can be stored on a smartphone, which then acts like a traditional card. Users can pay without carrying multiple cards in their wallets — all cards can be stored on the smartphone.
Business Benefits of Using NFC
Instant connection
NFC devices connect instantly for data exchange when brought close together. The small range of NFC chips makes this technology useful for payments, identification, access control, ticketing, or any other application requiring near-field data exchange.
Wireless exchange
All modern smartphones have NFC modules that connect wirelessly and without an external power source. NFC chips are passive devices that are powered by a device that reads them at the moment (this happens through magnetic induction).
Secure, standardized, and regulated technology
NFC data exchange occurs only between devices in close proximity. Nearby connection limited to one device protects the transaction from remote jacking by a hacker.
NFC connections are regulated by standard protocols like ISO/IEC 14443 A, ISO/IEC 14443 B, and JIS X6319-4. ECMA International, ETSI, and other authorities make sure that NFC is universally secure and accessible across device vendors.
No need for network connectivity
NFC tags can work without WiFi, 4G, 5G, or LTE connectivity. This means users can pay, transfer data, access areas, and use NFC-enabled services even while they’re disconnected from the internet.
For example, retail outlets and small businesses use NFC-enabled POS systems to process payments. Hotels use NFC keycards that work even in locations with a weak WiFi signal. Customers can use all the services without worrying about mobile data charges or signal unavailability.
Convenient and affordable technology
NFC tags are an easy and affordable technology that can help in digital transformation — contactless payments, access control, and identification can significantly improve customer and employee experience in their daily activities.
For example, you can use NFC to enable contactless access to your gym, health center, or office. Users can download your custom mobile app to pay for their membership and then use the smartphone to access the facility. In the post-COVID world, NFCs with digital tokens help any customer-facing business remain contactless.
Reduced carbon footprint
NFC is an eco-friendly solution that can minimize the carbon footprint of any business. Recyclable NFC tags made using paper reduce the use of plastic for access cards.
